Enamul Kabir1*, Shah Mohammad Bodruddoza2 and Masuma After3
1 Medical Officer, Department of Paediatrics, 250 Bed District Hospital, Magura, Bangladesh
2 Consultant (Paediatrics), Faridpur General Hospital, Faridpur, Bangladesh
3 Senior Consultant (Paediatrics), Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University (BSMMU), Dhaka, Bangladesh
*Corresponding Author: Enamul Kabir, Medical Officer, Department of Paediatrics, 250 Bed District Hospital, Magura, Bangladesh.
Received: May 08, 2023; Published: May 17, 2023
Citation: Enamul Kabir., et al. “Association between Antiepileptic Drugs and Therapy with Bone Mineral Density (BMD)”. Acta Scientific Paediatrics 6.6 (2023): 04-10.
Background: Epilepsy is a common medical and social disorder characterized by epileptic seizures. These seizures occur due to disruptions of electrical signals in the brain. Epilepsy also characterized by the neurobiologic, cognitive, psychological, and social consequences of this condition.
Aim of the study: The aim of the study was to find out the Association between Antiepileptic Drugs and Therapy with Bone Mineral Density (BMD).
Methods: This study was conducted in the Saleh Child Development and Disability Management Center (SCDDMC), of Institute of Child and Mother Health (ICMH) Matuail, Dhaka. A total of 31 childrens age ranged 5-15 years diagnosed as epilepsy on the basis of both clinical examination and investigation (EEG) receiving antiepileptic drugs (AEDS) for at least two years were recruited in this study.
Result: The mean serum calcium was 9.22 ± 0.78 mg/dl, and the mean BMD score of the spine was 0.66 ± 0.14. The mean BMD of the left femur neck was 0.66 ± 0.15. The name and combination of drugs used in the study children. It was found that 35.5% of the children received PB alone, followed by 16.1% receiving VPA alone. 12.9% received PB with VPA, 12.9% received PB with VPA with others, 9.7% received VPA with NTZ, and 6.5% received PB with VPA with NTZ and VPA alone. Table 7 demonstrated the association between the duration of drugs and the BMD Z-score of the study children.
Conclusion: AEDs decreased bone mineral density due to long term use as mono-therapy or polytherapy. The assessment of BMD among children with epilepsy receiving long term AEDs is essential.
Keywords: Bone Mineral Density (BMD); Epilepsy.
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder that affects millions of people worldwide, including Bangladesh. Epilepsy is a neurological disorder that affects approximately 50 million people worldwide, and the primary treatment for this disorder is the use of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). However, long-term therapy with AEDs has been associated with various adverse effects, including the loss of bone mineral density (BMD). Increasing the duration of treatment with antiepileptic drugs may increase the risk of osteopenia and fractures [1]. BMD is a critical determinant of bone strength, and its loss increases the risk of osteoporotic fractures. The association between AEDs and BMD has been studied extensively, and the findings are inconsistent. Some studies have shown a significant reduction in BMD, while others have reported no significant association [2,3]. Most patients require long-term and sometimes lifelong therapy with antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). AEDs are associated with significant side effects not limited to, radiological evidence of rickets but decreased bone mineral density (BMD), altered bone turnover, and increased risk of fracture [4]. Osteopenia is considered a silent disease because bone loss can occur gradually without symptoms. It occurs due to inadequate mineralization of bone [5]. Osteomalacia increases fracture risk. Bone mineralization begins at birth and plateaus in the third decade of life with subsequent gradual bone loss as a natural process of aging. Many of the effects of Osteomalacia overlap with osteoporosis [6]. Several studies have investigated the association between AEDs and BMD in Bangladesh. A cross-sectional study conducted by Rahman., et al. (2019) evaluated the BMD of 44 patients with epilepsy who were taking AEDs for more than six months [7]. The study found that patients who were taking AEDs had significantly lower BMD than those who were not taking AEDs. Similarly, a study conducted by Ahmed., et al. (2020) showed that the BMD of patients who were taking AEDs was significantly lower than those who were not taking AEDs [8]. Many studies reported a significant reduction in bone mineral density among children with epilepsy especially in patients receiving polytherapy treatment more than those on a single anti-epileptic drug [9]. Recent studies have suggested that the association between AED and BMD may be influenced by various factors, such as age, gender, duration of therapy, and type of AED use. Therefore, a personalized approach to AED therapy and BMD monitoring may be necessary to prevent the negative impact of AEDs on bone health [10]. The aim of the study was to find out the Association between Antiepileptic Drugs and Therapy with Bone Mineral Density (BMD).
This is a cross-sectional observational study, a total of 31 children enrolled and analyzed in this study. The study was conducted at the Department of Pediatric, Saleh Child Development and Disability Management Center (SCDDMC), Institute of Child and Mother Health (ICMH) Matuail, Dhaka. All the study children aged 5-15 years diagnosed with epilepsy based on both clinical examination and investigation (EEG) receiving antiepileptic drugs (AEDS) for at least two years were recruited in this study. All the relevant particulars were collected in a questionnaire data sheet. Clinical examinations including general and complete neurological examinations and investigations were done as per the standard procedure. Using a bone Densitometer (GY lunar-DPX-Central DXA scan, USA), the children’s lumbar spines (LV1–LV4) were examined. Using these normative data for study children as a reference for distribution, age and gender-specific Z-scores for all subjects were computed.
All data were presented in a suitable table or graph according to their affinity. A description of each table and the graph was given to understand them clearly. All statistical analysis was performed using the statistical package for social science (SPSS) program, and Windows. Continuous parameters were expressed as mean ± SD and categorical parameters as frequency and percentage. Comparisons between groups (continuous parameters) were made by Student’s t-test. Categorical parameters compared by Chi-Square test. The significance of the results as determined by a 95.0% confidence interval and a value of P<0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
The characteristics of the study children were presented in Table 1. It was noted that 61.3% of the children were aged between 5 to 10 years, while 38.7% were between 10 to 15 years. Most of the children, 74.2%, were male, and 25.8% were female (Figure 1). Nearly half of the patients’ fathers completed primary education, and more than half of the mothers completed secondary education. About 38.7% of the fathers were employed in service. All mothers were housewives. Consanguinity was observed in 25.8% of the children, and 22.6% had a family history of epilepsy (Figure 2).
Table 2 displayed the perinatal factors related to the study children. It was observed that 71.0% of the patients had NVD, and 29.0% had LUCS. Almost two-thirds, 64.5%, of the children had a history of perinatal asphyxia. Sunlight exposure and food habits of the study children were presented in Table 3. It was observed that more than two-thirds, 67.7%, of the children had adequate sun exposure, while 32.3% had inadequate exposure. Most of the children, 77.4%, had calcium and vitamin D-rich food intake for most days of the month, while 22.6% had intake only a few days of the month. The Anti-epileptic drugs used in the study children were shown in Figure 4. It was noted that 61.3% of the children had polytherapy, and 38.7% had mono-therapy. The mean serum calcium was 9.22 ± 0.78 mg/dl, and the mean BMD score of the spine was 0.66 ± 0.14. The mean BMD of the left femur neck was 0.66 ± 0.15 (Table 5). Table 6 presented the name and combination of drugs used in the study children. It was found that 35.5% of the children received PB alone, followed by 16.1% receiving VPA alone. 12.9% received PB with VPA, 12.9% received PB with VPA with others, 9.7% received VPA with NTZ, and 6.5% received PB with VPA with NTZ and VPA alone. Table 7 demonstrated the association between the duration of drugs and the BMD Z-score of the study children.
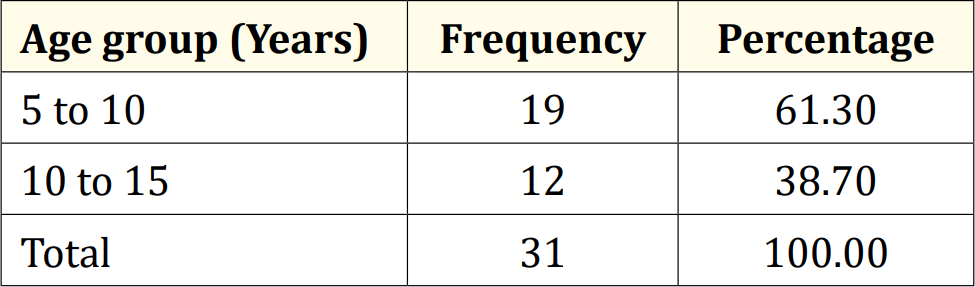
Table 1: Age distribution of the study children (N = 31).

Figure 1: Sex distribution of the study children.
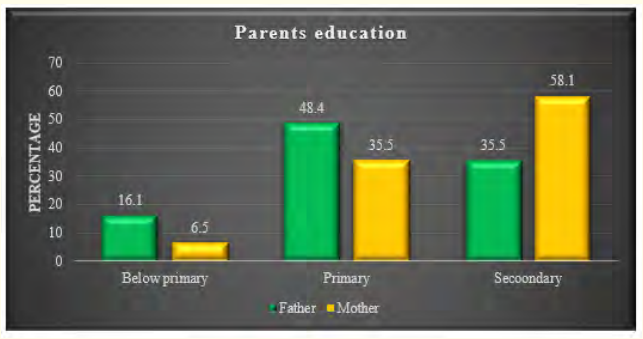
Figure 2: Parent’s educational status of the study.
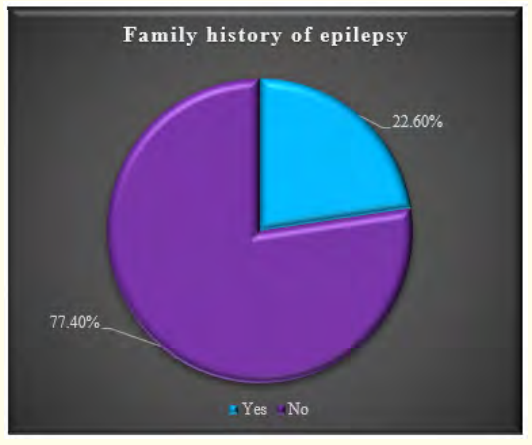
Figure 3: Family history of epilepsy.
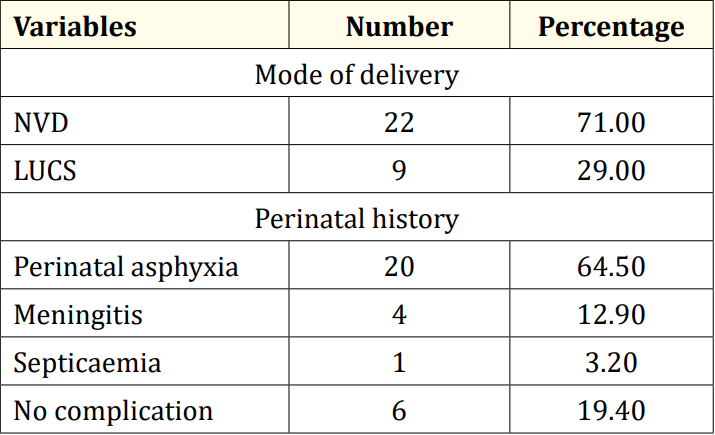
Table 2: Perinatal factors related to epilepsy (N = 31).
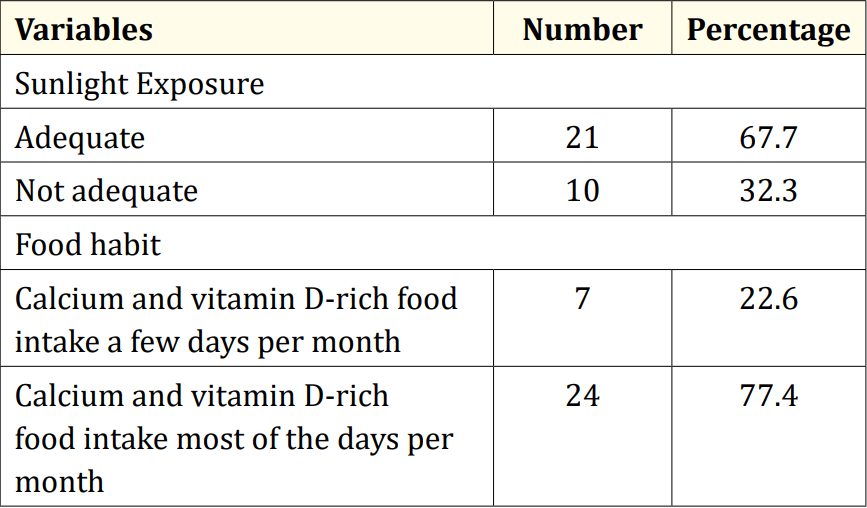
Table 3: Sunlight exposure and food habits of the study children (N = 31).
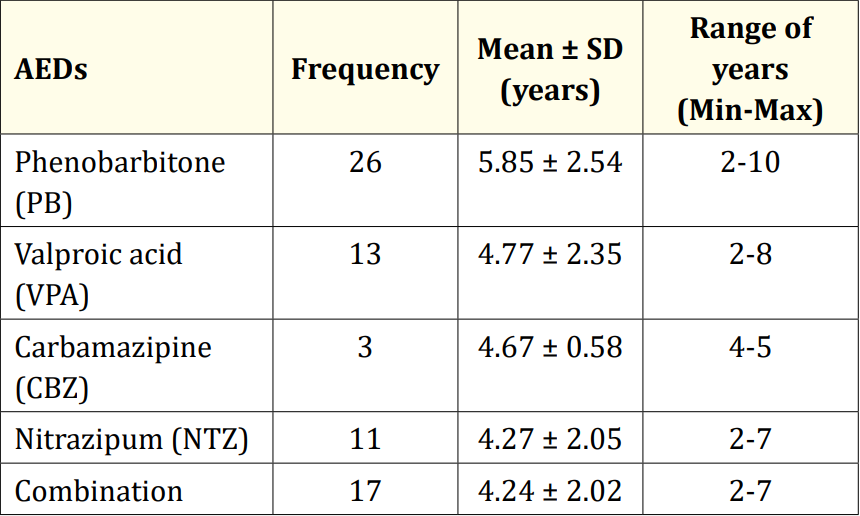
Table 4: Duration of AEDs used in study children (N = 31).
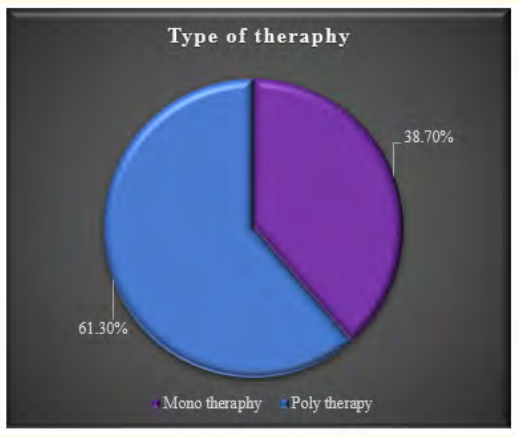
Figure 4: Type of anti-epileptic therapy used on study children.

Table 5: Serum calcium and BMD level of study children (N = 31).
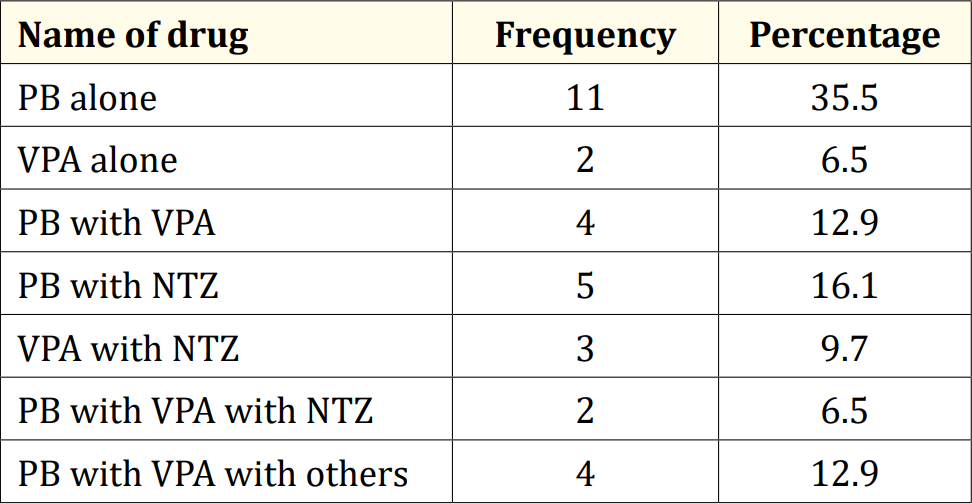
Table 6: Used drag combination of the study.

Table 7: Association between duration of drugs with BMD Zscore of the study children.
This study was done among epileptic children to asses BMD who were getting long-term AEDs total of 31 children were studied. In this study, regarding the socio-demographic characteristics of study children, it was shown that almost two third (61.3%) of children were in the age group 5 to 10 years followed by 12(38.7%) were 10 to 15 years. Almost three fourth (74.2%) of children were male and 8(25.8%) were female. More than one-fourth (25.8%) of children had consanguinity. Seven (22.6%) children had a family history of epilepsy. Hasaneen., et al. (2017) found that out of 70 epileptic children two third were in the age range between 3 and 13 years (mean age 7.7 ± 3.2 years), and almost two-thirds were male. These findings are nearly similar to the current study [11]. In another study, Osman., et al. (2017) observed that among 60 epileptic patients, 38 males (63.3%) and 22 females (36.7%) diagnosed as having epilepsy based on both clinical examination and investigation receiving antiepileptic drugs (AEDS) for at least one year [12]. Babtain (2013) observed that a family history of epilepsy (FHE) had a significant impact on the occurrence of epilepsy among offspring this may underlie the presence of a genetic etiology [13]. They also concluded that temporal epileptic discharges were the best predictor for FHE, which may suggest the presence of familial temporal lobe epilepsy. Similarly, Cansu., et al. (2007) reported that a positive family history of epilepsy increased the risk of developing epilepsy 4.75 times in their study [14]. In our study, it was observed that almost three fourth (71.0%) patients had NVD and 9(29.0%) were LUCS delivery. Almost two-thirds (64.5%) of children had a history of perinatal asphyxia. Perinatal asphyxia causing early brain injury might develop epilepsy in early childhood. Thomas., et al. (2011) observed out of 468 normal vaginal deliveries and 356 caesarean deliveries, 9 (1.9%) and 4 (1.1%) developed epilepsy later in the childhood period respectively [15]. In this study, regarding the sunlight exposure and food habit of study children, it was observed that more than two third (67.7%) of children had adequate sun exposure and 10(32.3%) had inadequate. More than three fourth (77.4%) of children had calcium and vitamin D-rich food intake most of the day per month diet and 7(22.6%) in calcium and vitamin D-rich food intake a few days per month. In a study conducted in Malaysia, Fong., et al. (2016) also observed that vitamin D deficiency is prevalent among pediatric epilepsy patients and one of the risk factors in those children was lower daily sun exposure behavior which correlates well with our study [16]. Moreover, they reported that a significantly high proportion of Malaysian children with epilepsy did not achieve the recommended vitamin D and calcium intake, with only 5.7% and 11.9% meeting the recommended vitamin D and calcium intakes respectively. In this study, epileptic children were treated with antiepileptic drugs. It was observed that almost two-thirds (61.3%) of children got polytherapy and 12(38.7%) got monotherapy. In a comparable study, Atugonza., et al. (2016) reported that forty-five of the 139 children (32.4%) were on multiple AED; 42 were on dual therapy while three were on triple therapy [17]. The most common drug combination was sodium valproate and carbamazepine, 34/45(75.5%) followed by carbamazepine and phenobarbitone, 6/45(13.4%) and sodium valproate and phenobarbitone, 2/45(4.5%). Of the 94/139 participants on monotherapy, 54/139 (38.8%) were on carbamazepine only, 37/139 (26.6%) were on sodium valproate only, two were on phenobarbitone and one was on phenytoin only. Regarding seizure control; of thirteen children on multiAED therapy, 13/45 (28.9%) had good seizure control compared to 61/94 (64.9%) patients on monotherapy. This study observed that common AEDs were used in study children. More than onethird (35.5%) of children got PB alone followed by 5(16.1%) got VPA alone, 4(12.9%) got PB with VPA, 4(12.9%) got PB with VPA with others, 3(9.7%) got VPA with NTZ, 2 (6.5%) got PB with VPA with NTZ and 2 (6.5%) got VPA alone. Epilepsy is the tendency to have recurrent, unprovoked seizures. Sarhan., et al. (2015) stated that although 70% of epileptic seizures can be controlled with monotherapy (treatment by a single antiepileptic drug), a combination of two or more anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) may be required to improve efficacy (seizure control) and tolerability [18]. Polytherapy (treatment with two or more AEDs) can affect efficacies and side effects in additive, supra-additive (synergistic) or infraadditive fashion. Many studies have shown a significant reduction in bone mineral density (BMD in patients treated with enzymeinducing antiepileptics (phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin) [4]. Increasing the duration of anti-epileptic drug treatment may increase the risk of osteopenia and fractures [1].
Every hospital-based study has some limitations and the present study undertaken is no exception to this fact. The limitations of the present study are mentioned. Therefore, the results of the present study may not be representative of the whole of the country or the world at large. The number of patients included in the present study was less in comparison to other studies. Because the trial was short, it was difficult to remark on complications and mortality.
In conclusion, the use of AEDs is associated with a decrease in BMD in patients with epilepsy in Bangladesh. Healthcare professionals should be aware of this association and monitor the BMD of patients who are taking AEDs. Appropriate calcium and vitamin D supplementation should be provided to prevent bone loss in these patients. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the relationship between AEDs and BMD. Clinicians should be aware of the potential for AEDs to impact bone health and consider monitoring BMD in patients on long-term AED therapy. Additionally, efforts to optimize bone health through measures such as adequate vitamin D and calcium intake, weight-bearing exercise, and smoking cessation should be encouraged in all patients with epilepsy, regardless of AED use. Overall, a multidisciplinary approach involving neurologists, endocrinologists, and bone health specialists may be necessary to address the complex interplay between AEDs and bone health.
No funding sources.
None declared.
The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee.
Copyright: © 2023 Enamul Kabir., et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
ff
© 2024 Acta Scientific, All rights reserved.